India’s Inflation Outlook: Historical Trends and Future Expectations

Source: shutterstock
Inflation is a key measure of India’s economic health, affecting spending and policy decisions. CPI trends over the past decade show notable fluctuations. This article reviews historical patterns and forecasts from SBI and RBI for FY26 and FY27.
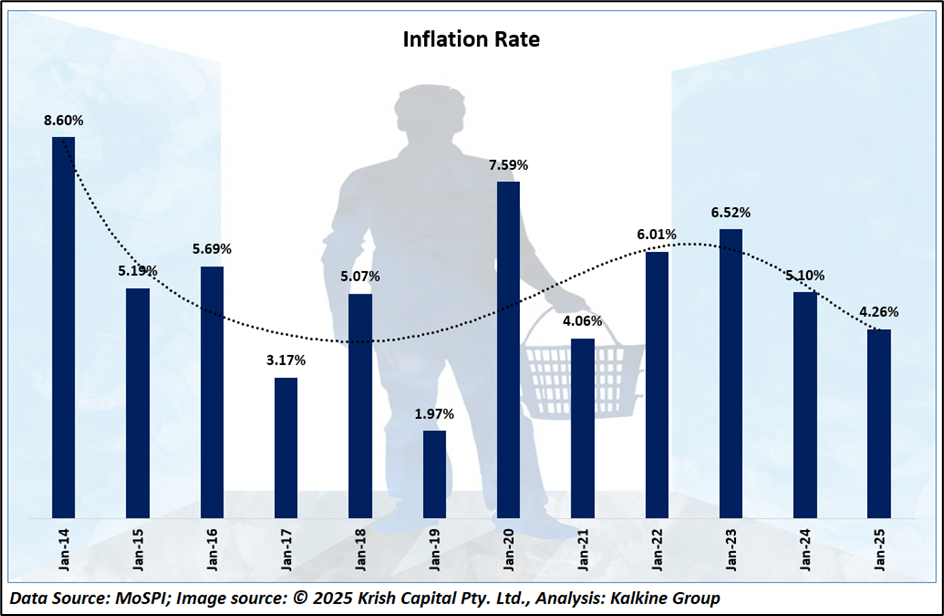
Historical CPI Inflation (2014–2025)
India has experienced notable fluctuations in consumer price index (CPI) inflation over the past decade. Starting from a peak of 8.6% in January 2014, inflation gradually eased in the following years, touching a low of 1.97% in early 2019. During the COVID-19 pandemic, inflation surged again, reaching 7.59% in January 2020. Since 2021, CPI inflation has been moderately stable, generally ranging between 3% and 7%, with variations largely influenced by food and energy prices.
SBI’s Outlook for FY26 and FY27
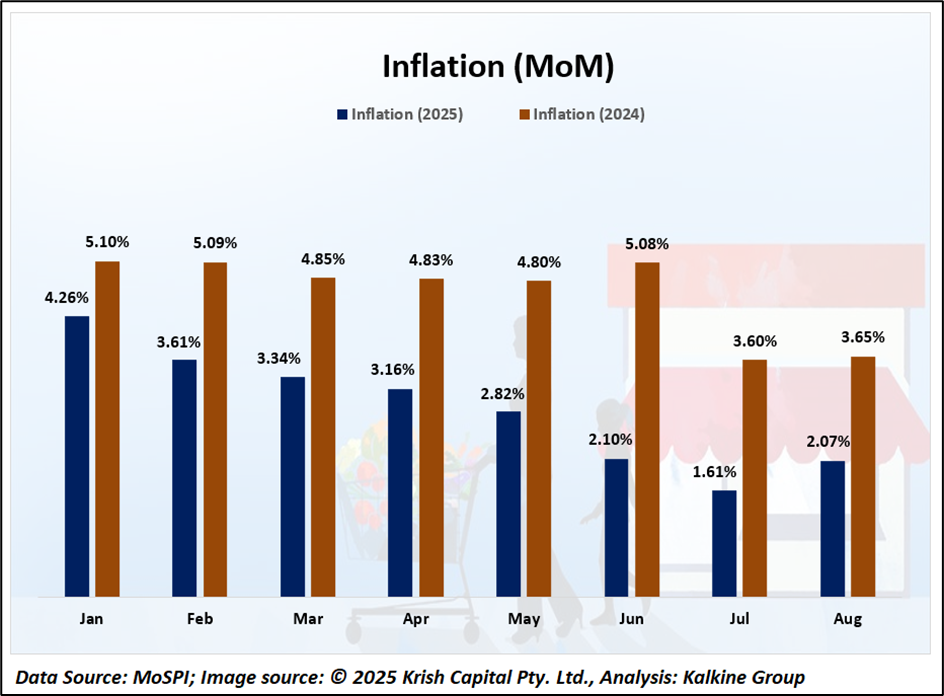
The State Bank of India (SBI) projects that inflation in FY26 and FY27 will be significantly lower than the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) current estimates. While RBI has revised its CPI forecast for FY26 to 2.6%, SBI anticipates that actual inflation could be even lower. Factors supporting this outlook include a favorable monsoon, increased sowing of kharif crops, adequate reservoir levels, sufficient foodgrain stocks, and rationalization of GST rates. For FY27, although RBI forecasts inflation at 4.5%, SBI expects the real numbers to remain below this projection, indicating a period of relatively stable prices.
RBI’s Inflation Projections
The RBI has recently adjusted its CPI inflation estimates downward for FY26, reflecting the easing of price pressures. This reduction aligns with the overall economic environment, including controlled supply-side constraints and stable domestic demand. The central bank remains vigilant, ready to implement necessary measures to maintain price stability, while considering the impact of global commodity prices and domestic factors.
Implications for Policy and Economy
India’s inflation history demonstrates resilience against external and internal shocks. With RBI maintaining a cautious monetary policy stance and ample liquidity in the system, the central bank is well-positioned to respond to unexpected developments. SBI’s report suggests that lower inflation could provide room for potential interest rate reductions in the coming years, though the timing and scale of such adjustments will depend on evolving economic conditions.
Conclusion
Overall, India’s inflation trajectory, supported by structural reforms and favorable domestic conditions, points toward a period of relative price stability in the near term. Both investors and policymakers are likely to monitor these developments closely as they plan for FY26 and FY27, taking into account historical trends and updated forecasts from SBI and RBI.
Disclaimer:
The information available on this article is provided for education and informational purposes only. It does not constitute or provide financial, investment or trading advice and should not be construed as an endorsement of any specific stock or financial strategy in any form or manner. We do not make any representations or warranties regarding the quality, reliability, or accuracy of the information provided. This website may contain links to third-party content. We are not responsible for the content or accuracy of these external sources and do not endorse or verify the information provided by third parties. We are not liable for any decisions made or actions taken based on the information provided on this website.
Copyright 2026 Krish Capital Pty. Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this website, or its content, may be reproduced in any form without our prior consent.